Lewis y
General | Antibody | Glycoprotein | Glycolipid | Enzyme | ReferenceEpitope information of EP0018
| Epitope ID | EP0018 |
|---|---|
| Epitope name | Lewis y |
| Structure | 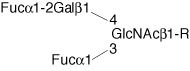 |
| Sequence | Fuc(a1-2)Gal(b1-4)[Fuc(a1-3)]GlcNAc(b1-)-R |
| Aliases | Ley,CD174, Y-hapten |
| History | Lewis antigens and their derivatives such as Leb,Lex,sialyl Lex,sialyl Lea,and Ley were identified as tumor-associated structures approximately 20 years ago using hybridoma technology and showed that upregulation and/or de novo expression of these determinants on the tumor cell surface is associated with a poor prognosis.[5] |
| DB | PDB:1S3K GlyTouCan:G00052MO JCGGDB |
| Molecular weight | 675.6 |
| Composition | (Fuc)2(Gal)1(GlcNAc)1 |
| Species | Homo sapiens |
| Tissue and Cellular distribution | cancer/ovary[2] |
| Subcellular distribution | |
| Developmental change | The Ley(CD174) are expressed on CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors but absent on mature lymphocytes and CD34- cell lines.[3] |
| Cell line | KG1 (CD34+ leukemia cell line)[3] |
| Receptor | |
| Function | The expression of the fucosylated histo-blood group antigen CD174 in CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells and down-regulation of FUT1 in mature lymphocytes may be important factors influencing the homing process of hematopoietic stem cells to the bone marrow.[3] |
| Diseases | AIDS/acquired immune deficiency syndrome[4] |
| Application | The Lewis antigen is expression in pancreatic cancer cells and may be useful as a tumor marker.[7] |
| Comment |

