| Epitope ID | EP0020 |
| Epitope name | T Antigen |
| Structure | 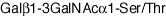 |
| Sequence | Gal(b1-3)GalNAc(a1-)Ser/Thr |
| Aliases | TF |
| History | Thomsen and Friedenrich found that essentially all human and animal sera contain antibodies against this cryptic antigen which is produced by bacterial or viral sialidase contaminated incidentally. This antigen is now called T or TF antigen after Thomsen and Friedenrich. |
| DB | PDB:1UGX
GlyTouCan:G00031MO
|
| Molecular weight | 383.4(Ser/Thr) |
| Composition | (Gal)1(GalNAc)1(Ser/Thr)1 |
| Species | Canis familiaris[37]
Homo sapiens
Macaca mulatta[20]
Mus musculus[14]
Rattus norvegicus[37]
Sus scrofa domesticus[37] |
| Tissue and Cellular distribution | cancer/breast[7][8][9][10][6][16]
cancer/breast(nipple aspirate fluid)[33]
cancer/colon[15]
cancer/colorectal[1][2][3][4][5][6]
cancer/esophageal[12]
cancer/liver[11]
cancer/ovary[6][16]
cancer/prostate[6]
cancer/stomach[29]
tumor/anaplastic meningioma[34]
tumor/bladder[13]
lymphocyte(mouse)[14]
T-lymphoid cell[17]
retinal neuron(dog)[37]
retinal neuron(pig)[37]
retinal neuron(rat)[37]
normal epithelia/breast[40]
stomach (monkey) [40]
subset of embryonic hemocytes(Drosophila)[42]
CNS/central nervous system (Drosophila) [42]
glomerular cell[43]
endothelial cell (pig)[43]
S2 cell/embryonal hematocyte-like Drosophila Schneider 2 cell(Drosophila) [44]
cancer(human)[45]
spermatocyte[38]
spermatid[38]
spermatozoa[38] |
| Subcellular distribution | testis/spermatocyte[38]
testis/spermatid [38] |
| Developmental change | rat fetus[18]
slight increase between 12 and 28 days of differenciation in BG01 human embryonic stem cells[46] |
| Cell line | Caco2/human colon carcinoma
HT-29/human colon adenocarcinoma[47]
MCF-7/human breast adenocarcinoma [35][39][47]
Sup T1
Ishikawa cell[39]
SW-48/human colon adenocarcinoma[47]
HCLE/human corneal-limbal epithelial[48]
HEK293/human embryonic kidney(transformed with EBNA-1 gene)[49] |
| Receptor | ABA/Agaricus bisporus agglutinin [50]
Artocarpus hirsuta lectin [51]
AVL/Amaranthus viridis lectin [52]
BPA/Bauhinia purpurea agglutinin[53]
CBL/Clarias batrachus lectin[54]
galectin-9 [55]
galectin-3[19][56]
galectin-1[57]
HPA/Helix pomatia agglutinin[58]
HSL/sea cucumber Holothuria scabra [59]
jacalin[60][61][62][51]
MGL/macrophage galactose-type lectin(human)[41]
MGL2/macrophage galactose-type lectin(mouse)[41]
MPA/Maclura pomifera[63]
MPL/Maclura pomifera lectin [64]
PNA/Arachis hypogaea (peanut) lectin [65][64]
SRCL/scavenger receptor with C-type lectin/CL-P1/collectin placenta 1[49] |
| Function | accumulation Lipoprotein(a) or LDL within arterial walls in atherogenesis [66]
cancer progression (increase interaction/communication of the cells) [45]
T antigen expression in RMA lymphoma cells leads to a reduced growth of the tumor.[67]
correlation with elevated Golgi pH in cancer cell (breast, colorectal cancer cells)[47]
T antigen on apical surfaces of corneal epithelial cells provide protection against rose bengal penetrance.[48]
reduction of a flexibility of the glycosidic bond and thereby favour certain glycan conformation[68]
T antigen is a target for NK cell-mediated lysis[69]
inverse relationship between T antigen expression and VWF plasma levels[70] |
| Diseases | anaplastic meningioma[34]
breast cancer[7][8][9][10][6][16][33]
colorectal cancer[1][2][3][4][5][6]
colon cancer[15]
esophageal cancer[12]
gastric cancer[29]
liver cancer[11]
ovarian cancer[6][16]
prostate cancer[6]
bladder tumor[13]
invasive pneumococcal infection (hemolytic uremic syndrome, hemolytic anemia) [71] |
| Application | useful marker for anaerobic bacterial infection[72] |
| Comment | |